Blue Carbon, Risk Reduction
and Climate Adaptation
Blue Carbon, Risk Reduction
and Climate Adaptation

Blue Carbon, disaster risk reduction and climate adaptation
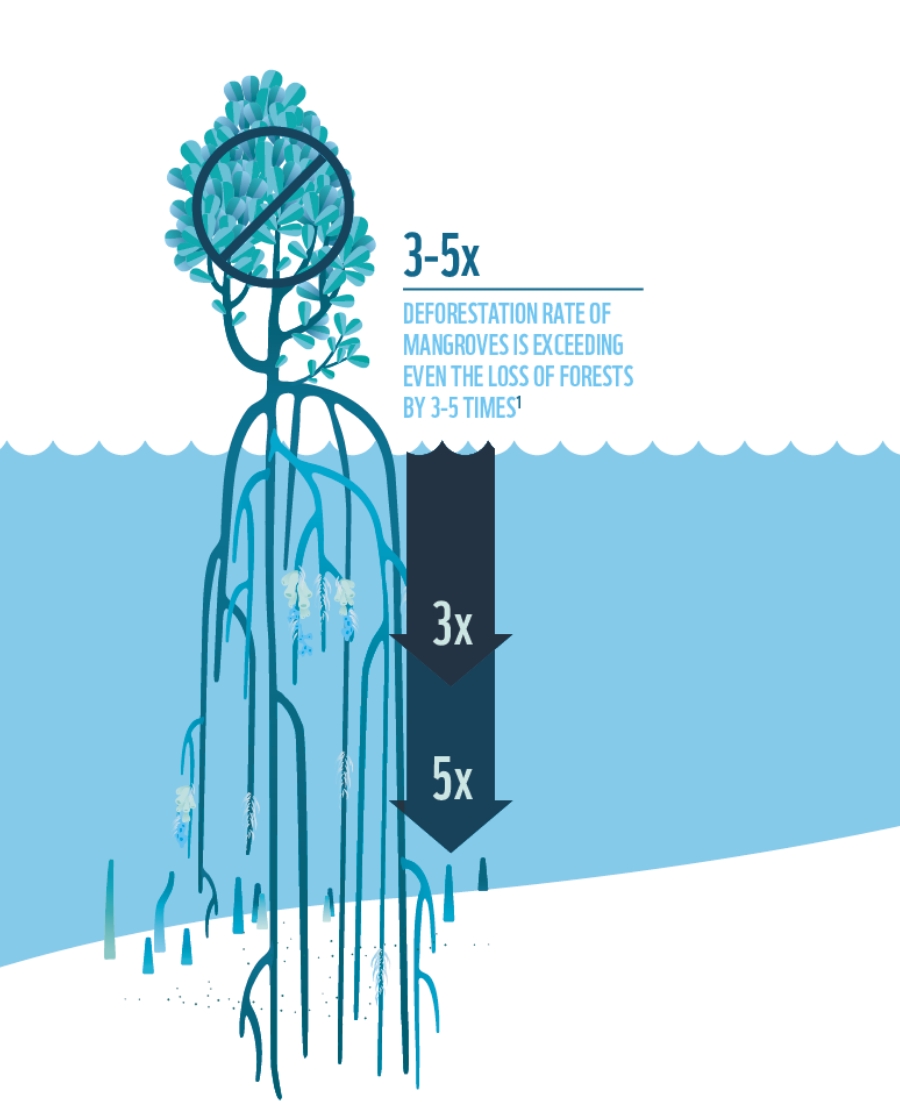
Mangroves are highly productive coastal ecosystems, with soil carbon sequestration rates per hectare up to 10 times larger than those of terrestrial ecosystems.
The protection of blue carbon ecosystems offers an efficient pathway to avoid CO2 emissions, particularly for places with large areas of coastal vegetation and high rates of loss, because:
- while they are equivalent to only 1.5% of terrestrial forest cover, their loss and degradation are equal to 8.4% of CO2 emissions from terrestrial deforestation.
- the stored carbon degraded ecosystems become oxidised and releases back into the atmosphere.
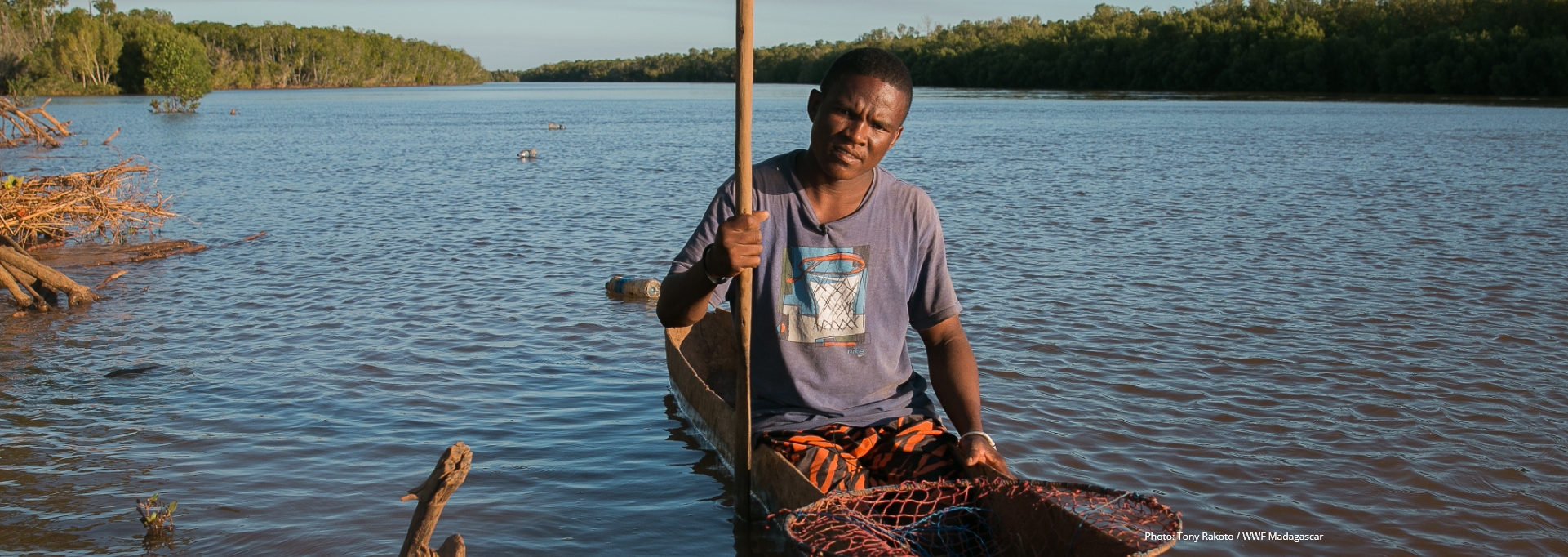
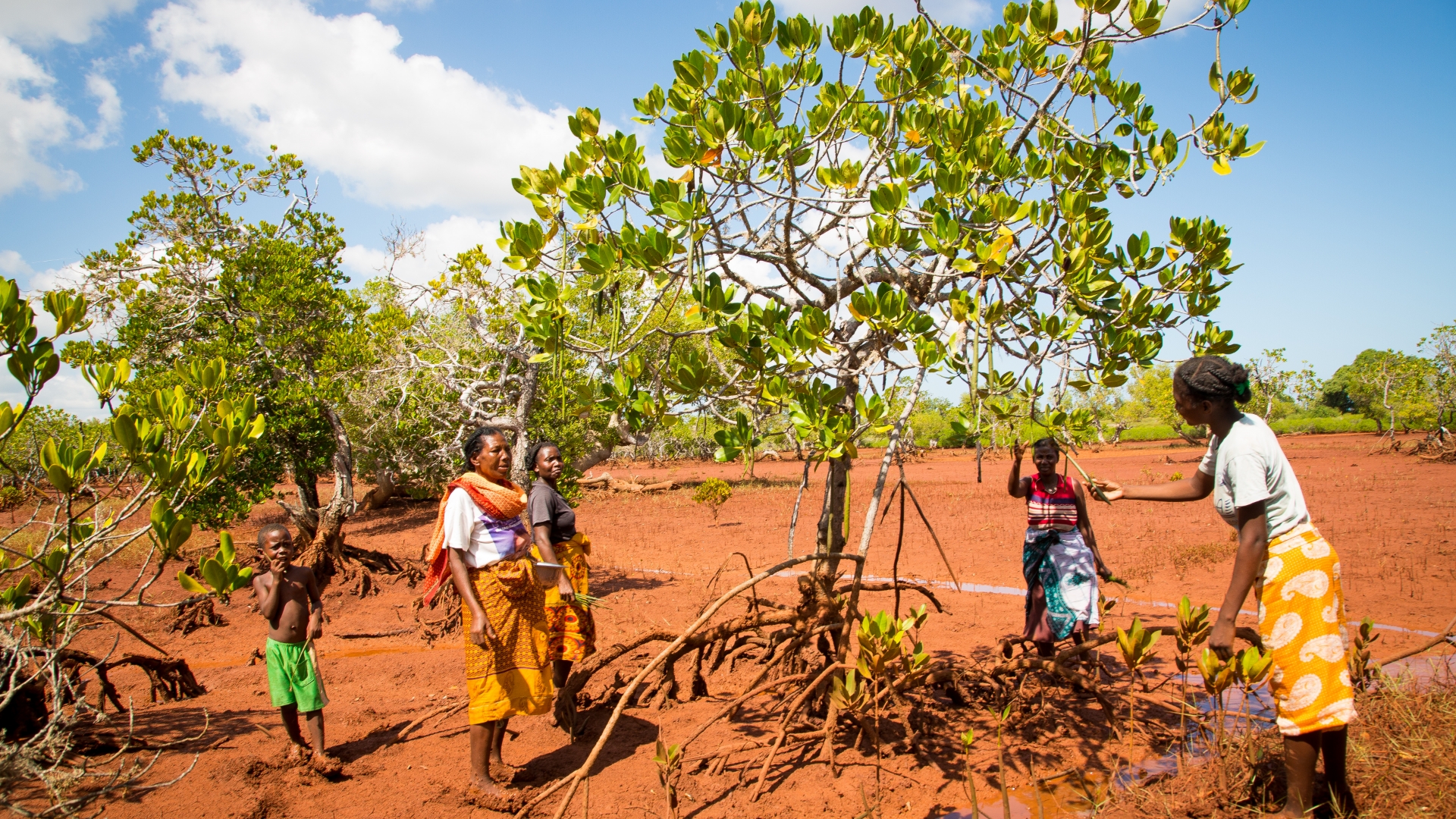
On-the-ground management of coastal and marine ecosystems often depend on coastal communities, yet the degradation of blue infrastructures, such as mangroves, leave these communities vulnerable to the effects of extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
It is both unrealistic and unfair to expect them to conserve these ecosystems for the globe without support, including investment, from the broader global community.
Pilot.
- Primary: Blue carbon credit sale.
- Secondary:
– Product sales (honey, fish/crab) and mangrove conservation tourism.
– Future cost saving (in terms of emergency relief and reconstruction post event).
– Potential for insurance – Financial viability of insurance still to be determined (most likely sovereign parametric insurance).
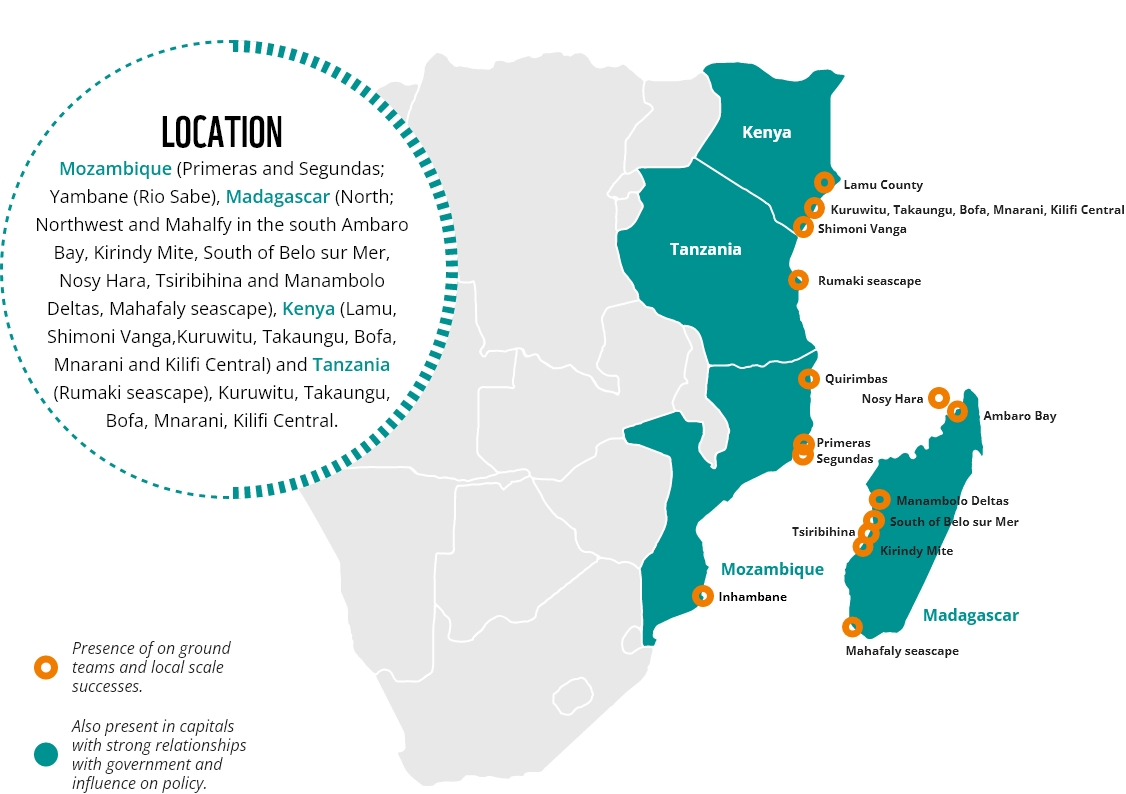
Local stakeholders, including businesses, communities and government.
Agence Française de Développement (AFD), Blue Action Fund, KfW, BMZ (German government).
PCI Media, Adel Sofala, Kukumbi, Wetland International, Save Our Mangroves Now, IUCN and Eduardo Mondlane University.
Access to funding and implementation support to the communities.
+ Already revenue generating.
– Carbon certificates from mangrove conservation are still in pilot phase.
Expected profitability
| country | TOTAL MANGROVE COVERAGE | TOTAL RESTORABLE AREA | GLOBAL RESTORABLE AREA | CARBON SEQUESTRATION POTENTIAL | EXPECTED RETURN AT CARBON PRICE OF USD 60 PER TONNE | FLOOD PROTECTION BENEFITS | INCLUSION OF MANGROVES IN NDC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hectares | Hectares | % | Million tonnes of CO2 | USD billions | USD billions | Adaptation/ Mitigation | |
Mozambique |
294 | 25.9 | 3.3 | 8 | 66 | 1.94 | No |
Madagascar |
261 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 57 | 0.36 | Yes - A & M |
- Distaster risk reduction.
- Job creation.
- Improved livelihoods.
- Carbon sequestration.
- Mangroves provide nursery grounds for commercial and food fish.
- Reduced coastal erosion.
- Technical assistance for community engagement.
- Development of technical mangrove restoration skills.
(infrastructure and market building)
- Technical assistance for market access.
- Improvement of road access for collectors (fish/crab), preservation equipment (cold chain) and shipment of goods (Chinese trade).
High – where similar conditions exist (most regions).
- Monitoring system reliability and scalability (MOMS).
- Difficulties to certify direct link from conservation actions and actual carbon sequestration.
- Greenwashing from carbon voluntary markets.
- Crab fisheries require very quick collection and shipping (highly perishable goods).
- Improved crab fishery resource management needed.
IF YOU ARE INTERESTED IN SUBMITTING A PROJECT OR INVESTING IN ONE OF THE PROJECTS PROFILED ON THIS PLATFORM, THEN PLEASE COMPLETE THIS FORM AND WE WILL BE IN TOUCH SHORTLY.



